Recommendation Tips About How To Choose Level Of Significance

For p (h0)=0.5 we obtain different ideal levels for the significance and the power level depending on the associated costs:
How to choose level of significance. Cance levels and how to report them : ( 1 ) think and reflect on. The level of significance is the probability that we reject the null hypothesis (in favor of the alternative) when it is actually true and is also called the type i error rate.
The result of a hypothesis test, as has been seen, is. Step 3 in the five steps of hypothesis testing is to select a level of significance. The steps to find the level of significance is listed below.
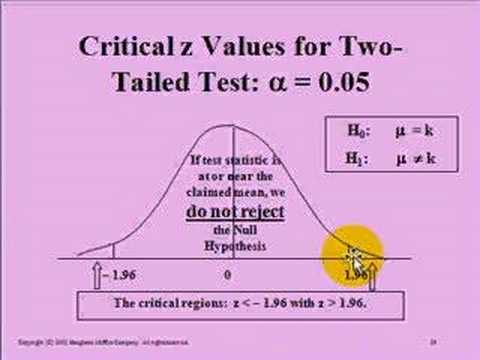
Common significance levels are 0.10 (1 chance in 10), 0.05 (1 chance in 20), and 0.01 (1 chance in 100). How to choose the level of significance: The level of significance sets a “fence” that we use to determine if our.
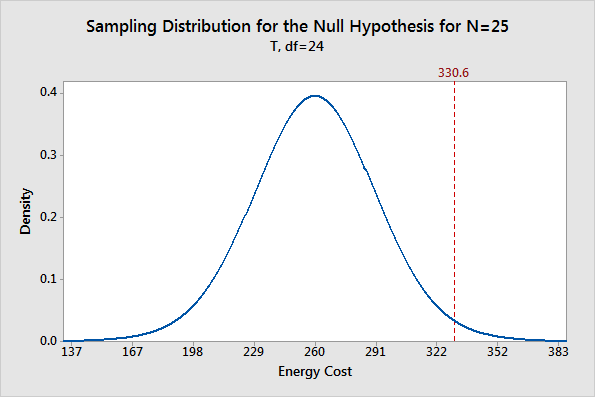
The level of significance should be chosen with careful consideration of the key factors such as the sample size, power of the test, and expected losses from type i and ii errors. A particularly difficult parameter to tune is often the level of statistical significance. When n = 300, setting = 0.015.
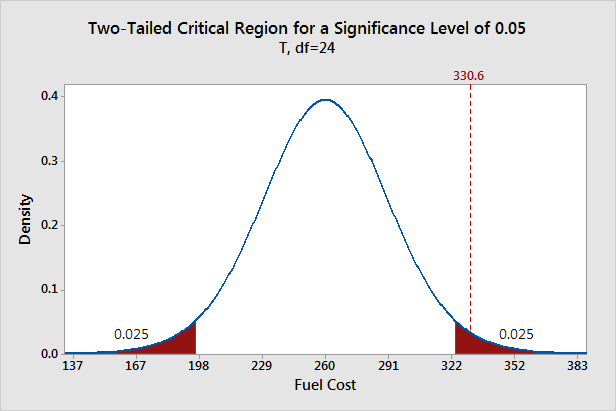
The level of significance should be chosen with careful consideration of the key factors such as the sample size, power of the test, and expected losses from type i and ii errors. = 0.05, the power of the test is only 0.20. Yet, it is far not always clear how to choose the parameters for the test.
Is set at 0.35, the power of the test is 0.65. The level of significance should be chosen with careful consideration of the key factors such as the sample size, power of the test, and expected losses from type i and ii errors. The arbitrary nature of conventional levels of significance, (2) report the.
![Pdf] How To Choose The Level Of Significance : A Pedagogical Note | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/0b22bc4444f9b2a5a5b007fba2d75a95d3789e49/12-Table2-1.png)





![Pdf] How To Choose The Level Of Significance : A Pedagogical Note | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/59a74f2eeb56d53bcad56970a016516c695cd0f6/12-Table1-1.png)